Clogged pores are a common skin concern that may lead to acne. A buildup of dirt, oil or dead skin cells can cause clogged pores. The condition is most common in people with very oily skin. A gentle skin care routine can help resolve clogged pores.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.
What are clogged pores?
Clogged pores develop when dead skin cells, oil or dirt get trapped in your pores. Pores are tiny openings in your skin that release oil and sweat from your glands. Clogged pores can lead to acne.
Clogged pores are common on people’s faces. However, they can occur anywhere on your body, including your scalp, neck, back, shoulders and chest.
What’s the difference between clogged pores and enlarged pores?
Clogged pores and enlarged pores aren’t the same things, but they’re often related. Clogged pores can be the result of your glands producing too much oil. More oil on your skin increases the risk of clogged pores. But lots of other things can lead to enlarged pores, including age, skin products, hair follicles and sun damage. So enlarged pores don’t always lead to clogged pores.
Who gets clogged pores?
Similar to acne, clogged pores tend to be more common in adolescents and young adults. During puberty, hormones stimulate the glands that produce oil. But anyone of any age or gender can get clogged pores.
Having a family history of acne or clogged pores can also increase your risk of having the same skin concerns. Sometimes you inherit genes from your parents that make you more likely to have very oil or dry skin.
How common are clogged pores?
Clogged pores are very common. Acne affects about 50 million people each year, and clogged pores are the leading cause of acne.
Symptoms and Causes
What causes clogged pores?
A buildup of dead skin cells, oil or dirt can clog pores. Possible causes include:
- Dry skin or skin that produces extra skin cells.
- Face products, like cleansers, lotions or cosmetics.
- Medications that change how much oil your glands produce.
- Oily skin due to your age, hormones or genetics.
Some things that don’t directly cause clogged pores, but can make them worse, include:
- Certain foods.
- Clothing, backpacks, helmets or other garments or equipment that rub against your skin.
- Humid conditions.
- Picking at pimples.
- Pollution.
- Stress and anxiety.
- Washing or scrubbing your skin too hard.
What are the symptoms of clogged pores?
Most people notice clogged pores only when they lead to one of the following skin concerns:
- Whiteheads: A clog in the opening of a pore can cause a raised white or flesh-colored bump on the skin. Another name for a whitehead is a closed comedo (closed pore) or a zit.
- Blackheads: A clog that widens the opening of the pore is a blackhead. Blackheads don’t look black because of dirt; it’s the chemical reaction of the pore’s content mixing with oxygen that makes them appear black. Another name for a blackhead is an open comedo (open pore). A very large blackhead is a dilated pore of Winer. It appears as an opening in your skin, filled with a blue or black substance.
- Pimples and pustules: A lot of dirt and oil inside a pore can lead to redness, swelling and irritation. Whiteheads and blackheads are types of pimples. Pimples are also called papules. If they contain pus, they’re pustules.
- Nodules and cysts: A very clogged pore can cause swelling, pain and irritation deep in the skin. If a nodule contains pus, it’s called a cyst. Cystic acne can lead to acne scars.
Diagnosis and Tests
How are clogged pores diagnosed?
There isn’t a test for clogged pores. Your healthcare provider examines your skin and reviews your medical history. They may also ask you about your:
- Current medications.
- Family medical history.
- Skin care routine.
Management and Treatment
How are clogged pores treated?
Most people can manage mild to moderate clogged pores by:
- Applying non-comedogenic face products: The term “non-comedogenic” means a product won’t clog pores. Look for cleansers, cosmetics and moisturizers that say “non-comedogenic” or “oil-free” on the label.
- Cleansing and moisturizing your skin regularly: Gently wash your face twice each day with a non-comedogenic cleanser and warm (not hot) water. Use an oil-free moisturizer after cleansing to avoid dry skin.
- Using products that contain retinol or salicylic acid: Retinol and salicylic acid help clear out dirt, oil and other debris clogging your pores. Some people find that these ingredients irritate their skin. Talk to your healthcare provider before using products that contain retinol or salicylic acid.
Prevention
How can I prevent clogged pores?
You can help prevent clogged pores by sticking to a skin care routine that’s right for your age, skin type and skin concerns. A dermatologist (medical doctor who specializes in skin conditions) can recommend the right products and treatments.
Other ways to prevent clogged pores include:
- Avoid touching your skin with unwashed hands.
- Don’t use oil on your face, such as coconut oil, olive oil or jojoba oil.
- Exfoliate your skin with gentle scrubbing or periodic chemical peels.
- Keep your skin clean and moisturized.
- Never pick at or pop pimples.
Outlook / Prognosis
What can I expect if I have clogged pores?
Clogged pores aren’t usually cause for alarm. They usually clear up with the right skin treatments. If you’re concerned about pimples or other blemishes caused by clogged pores, talk to your healthcare provider.
Living With
When should I contact my doctor?
Contact your doctor if you have acne that is painful, inflamed, infected or filled with pus. You should also reach out to your provider if you notice any abnormal skin growths or lesions.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Clogged pores are a common skin condition caused by a buildup of dead skin cells, oil or dirt. Clogged pores can lead to acne, but they’re fairly easy to treat. Regular cleansing with non-comedogenic skin care products usually resolves clogged pores. Some people need special skin ointments that contain retinol or salicylic acid.
What are blackheads?

Blackheads are a type of acne that develops when hair follicles become clogged.
When the opening of a pore (hair follicle orifice) becomes blocked with sebum (oil) and dead skin cells that then solidify, the surface color often darkens. This is what is commonly called a blackhead. There are several skin conditions in which blackheads are an important component. The medical name of this structure is a comedo (plural: comedones).
What do blackheads look like?
Blackheads usually look like small, dark or black bumps on the skin. They can usually be 1-3 millimeters in diameter. They can appear gray, brown, or black. Blackheads may be flat or slightly raised, giving the skin a rough texture. Sometimes, a blackhead may look like an enlarged pore.
Characteristics
- Blackheads are open bumps on the skin that fill with excess oil and dead skin cells.
- They form when hair follicles become clogged with a combination of sebum (an oily substance produced by sebaceous glands), dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria.
Color
- Blackheads have a dark appearance and are typically noticeable against the surrounding skin.
- The dark color of a blackhead is not caused by dirt, as is a common misconception. Instead, it is due to a chemical reaction known as oxidation, where oxygen in the air reacts with the skin pigment melanin. This reaction causes the contents of the clogged follicle to turn black.
Size and shape
- Blackheads are generally small, ranging from a pinpoint to a few millimeters in diameter.
- The top of the blackhead, which is exposed, can sometimes appear larger than the clogged pore itself.
- They can appear as individual bumps or in clusters, often on the nose, chin, and forehead.
Location
- Blackheads typically occur on areas of the body with a high concentration of hair follicles and sebaceous glands, such as the face, chest, and back.
- Less commonly, they can appear on other areas such as the neck, arms, and shoulders.
Texture
- Blackheads can feel rough or gritty due to their hardened surface.
It is essential to avoid squeezing or picking at blackheads, as this can cause further breakouts and even scarring. A consistent skin care routine and gentle, effective products can help manage and prevent blackheads.
Blackheads vs. whiteheads (pimples)
The black color of the surface of the comedo is thought to be due to the oxidation of the fat molecules in the sebum. If the surface of the comedo is covered by skin, this oxidation does not occur and the structure might be called by some “a whitehead” or pimple. This terminology could be confused with a pustule, which may often occur at or near a follicular orifice.
What are the causes and risk factors for blackheads?
Blackheads are most often recognized early in the course of acne vulgaris, the inflammatory skin disease that affects the face, back, and chest of almost all teens as they go through puberty. They are thought to be the first sign of teenage acne and contain inflammatory substances that start the acne process.
Common causes of blackheads include:
- Elastotic degeneration of the skin affects sun-exposed areas, mostly on the face. The yellowish bumpy deposits of degenerated collagen are often accompanied by numerous blackheads.
- Chloracne is a condition caused by the absorption of dioxins, which are well-known toxins often encountered as a byproduct in the manufacture of herbicides and defoliants.
- Certain topical hair products are known to induce blackheads on the adjacent skin, resulting in a condition called “pomade acne.”
- Makeup and other cosmetics occasionally may contain comedogenic substances.
- Comedones are seen on the exposed skin of certain workers exposed to insoluble cutting oils in the metal machining industry.
- Certain anti-seizure and antipsychotic medications are thought to induce comedones.
- Certain rare birthmarks called epithelial nevi may contain many blackheads.
- Sometimes, a follicular orifice may become so dilated that after it becomes filled with dried sebum and skin, it is termed a “giant pore of Winer.”
What are the symptoms of blackheads?
Blackheads rarely produce symptoms in themselves. Blackheads often are a sign of some of the previously listed skin conditions. Most of the time, these little black dots are of no significance aside from their cosmetic appearance, which is dramatically enhanced when using a magnifying mirror.
When symptoms of blackheads do appear, they may appear as the following:
- Small black or yellowish bumps
- Often found on the face
- May be widespread across the back, chest, arms, and legs
- May appear with whiteheads, papules, pustules, cysts, or nodules
Cysts, papules, and nodules may feel tender and painful, but blackheads usually do not hurt.
What types of specialists diagnose and treat blackheads?
You do not have to be a specialist to recognize a blackhead. Occasionally, a magnifying glass can be helpful. If they become a bothersome problem, a dermatologist may see you for treatment strategies. A dermatologist specializes in the treatment of acne and other skin diseases and conditions.
How do health care professionals diagnose blackheads?
A health care professional, most often a dermatologist, will likely be able to explain which skin condition is responsible for producing the blackheads.
Blackheads can usually be identified by their unique appearance. Your clogged pore will have a dark spot in it. It may or may not be raised, and it has an opening. A dark spot on your skin may not always be a blackhead, so if you have trouble identifying the dark spot on your skin, your doctor can perform a physical examination to determine what it is.
If your dark spot isn’t a blackhead, your doctor may take a sample of it, send it to a lab, or refer you to a dermatologist for further diagnosis.
Health News
- Medicaid Covers GLP-1 Meds for Obesity in Just 13 States
- Why Treatments Can Fail Folks With ‘Wet’ Macular Degeneration — and What Might Really Work
- Banning Menthol Cigarettes Might Drive Smokers to Quit-Smoking Therapies
- A Visit to the ER Can Often Precede a Cancer Diagnosis
- In a National First, an Idaho Health Department Is Refusing to Give COVID Vaccines
 More Health News »
More Health News »
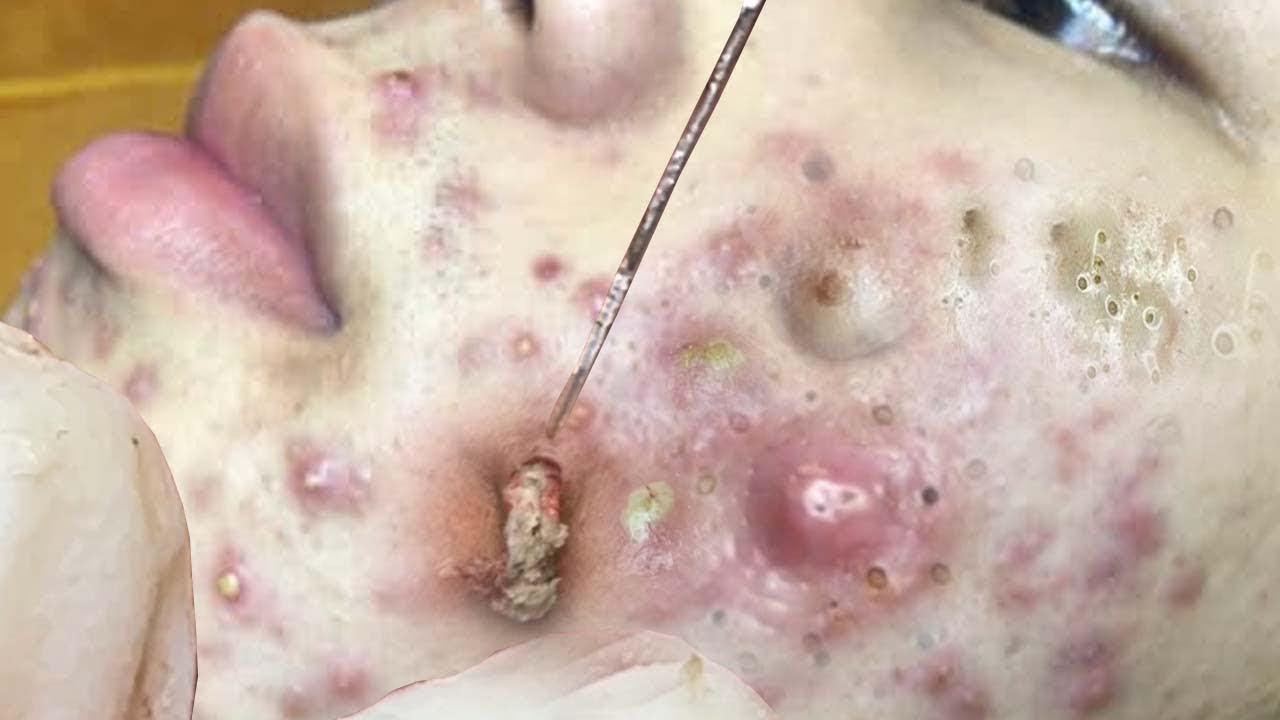
What are the types of treatment options for blackhead removal?
If blackheads are a significant problem, it may be necessary to apply a prescription topical retinoid like tretinoin (Refissa, Atralin, Tretin-X) or tazarotene (Tazorac, Avage) to successfully get rid of the blackhead.
Occasionally, physicians may remove a blackhead. Most often, this procedure is performed by a trained esthetician, a skin care specialist, who ought to be able to get rid of the blackhead without damaging the adjacent skin.
Are there home remedies that get rid of blackheads?
Here’s how to get rid of blackheads. Salicylic acid pads and/or 12% ammonium lactate lotion can be found in most pharmacies. They contain a chemical that exfoliates or loosens the blackheads on the face so that it is possible to remove them while washing the face.
Here’s how to remove blackheads naturally at home. Comedo extractors can be purchased from most pharmacies and internet retailers. These small metallic devices have a small opening in a spatula-like tip, which when pressed over the blackhead produces enough side pressure on the skin to get rid of the oil plug from the blocked pore. This might not be the best option because an untrained operator (the patient) may be too aggressive and produce more damage than benefit.
Other options for comedo removal include vacuum suction and pore strips. There is little compelling evidence that blackhead removal produces any lasting benefit.
What is the prognosis for blackheads?
Since most blackheads are due to acne, which is limited to puberty in most people, it is likely they ultimately will resolve spontaneously.
What are the complications of blackheads?
Blackheads are clogged pores that still have an opening. They can become irritated if you scratch or try to squeeze the blackhead out. If you don’t disinfect the area before and after you get the blackhead out, bacteria can get into the pore and cause an infection. If pores are infected, the skin can become inflamed and cause acne, which is the inflammation that results from clogged pores.
The pores can also become inflamed if the blackhead isn’t treated. Other conditions can occur as a consequence of the inflamed tissue if you insist on popping blackheads and pimples yourself. Scarring can occur if a pimple is recurring and you continuously pop it. The scars are usually pitted and sometimes remain as a dark red mark.
Hyperpigmentation can happen as the wounded skin heals. Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, can collect in the healing area and cause it to heal as a dark spot. If you have a pimple, blackhead, or acne and dark spots occur after it is gone, it is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Keloidal scars can form from acne. These are raised scars that occur if the scar tissue overgrows in the area. Keloidal scars can become quite large as the scar tissue continues to grow over time.
If you’ve been given medication for your blackheads or acne, there may be some mild side effects such as dry or irritated skin, which is usually treated with moisturizers. Oral contraceptives may sometimes be prescribed to treat acne and can cause other side effects. Your doctor will discuss the effects with you if they feel you need them for treatment.
Is it possible to prevent blackheads?
Blackheads may be prevented by treating the skin condition responsible for their presence. This is most effectively done by a dermatologist.
Additionally, to prevent blackheads:
- Use alcohol-free skin products.
- Wash your face after waking up, before going to bed, and after exercising.
- Shampoo oily hair regularly.
- Use sunscreen or sunblock before stepping out in the sun.
- Change pillowcases often.
- Limit the number of times you touch your face.
- Apply nonabrasive cleansers on the skin gently.
- Use water-based makeup products.
Frequently asked questions
- Is it good to remove blackheads? It is good to remove blackheads to prevent clogged pores and reduce the risk of acne, but it’s important to do it safely to avoid skin damage or infection. Over-the-counter treatments with salicylic acid or manual removal by a dermatologist are recommended.
- Is it OK to squeeze blackheads? It is generally not recommended to squeeze blackheads. Squeezing can cause scarring, increase the risk of infection, and push the blockage further into the skin, making it harder to remove. Instead, it is advised to use gentle cleansing and topical treatments to help clear blackheads safely and effectively. Consult a dermatologist before using any topical treatments.
- Can soap remove blackheads? Soap alone is not typically effective for removing blackheads. For best results, use products containing salicylic acid or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) to break up the oil plugs in the pores. Additionally, charcoal soap may help reduce blackheads due to its ability to draw out impurities. For blackhead removal, professional treatments are more effective.
- How do you remove deep blackheads? Deep blackheads typically require professional extraction, as they can be difficult to resolve on their own. Topical treatments such as salicylic acid, retinol, and glycolic acid can help soften and break down blackheads, but deep blackheads often require manual extraction by a dermatologist or other skin care professional.
- Can you get blackheads on your lips and behind your ears? Blackheads can occur on the lips and behind the ears. They are a type of non-inflammatory acne caused by clogged pores with oil, dead skin cells, and dirt. Blackheads can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, neck, back, chest, and even on the lips and ears.